Since Zamak became a sought after alloy in the manufacturing space, its unique properties have made it the best fit for several applications. As such Zamak die casting is a prerequisite for building several intricate parts for diverse industries. In this article, we’ll explain the fundamentals of this process, its benefits, shortcomings, and numerous use cases. Read on!
What Is Zamak Die Casting?

Zamak die casting is a widely known manufacturing process that involves creating near-net-shape components with ultra-complex geometries. This process is achieved by injecting a molten metal forcefully into a die casting mold and allowing it to solidify. Zamak die casting can produce highly detailed and dimensionally accurate parts that might not need a surface finishing in just a few seconds.
There are different types of Zinc die casting which include HPDC, LPDC, and gravity. The HDPC, also high-pressure die casting for Zamak alloy, is a very fast process that can produce up to 1000 parts per hour. It helps manufacturers churn out high-volume, high-precision components at incredible speeds.
This feature has made Zamak die casting more valuable for industries like automotive and electronics, where mass production with tight tolerances is critical. Additionally, Zamak 3 and Zamak 5 are the two types of Zamak alloy materials used for die casting that provide the best results.
Manufacturing Processes of Zamak Die Casting
Die Design and Manufacturing
In die casting, the first step is to design, generate, and manufacture the die-cast. Casts are usually made of high-grade steel tools that can withstand very high temperatures and pressures.The die includes channels for metal flow, air vents, and cooling systems to regulate temperature when casting Zamak.
Melting and Preparation of Zamak Alloy
During the preparation of the materials used for die casting, ensure that impurities are removed in order to enhance the quality of the final component. At this stage, the Zamak metal material is melted in a furnace at approximately 385-450°C. It is important to maintain this temperature throughout the metal die casting process to prevent defects during injection.
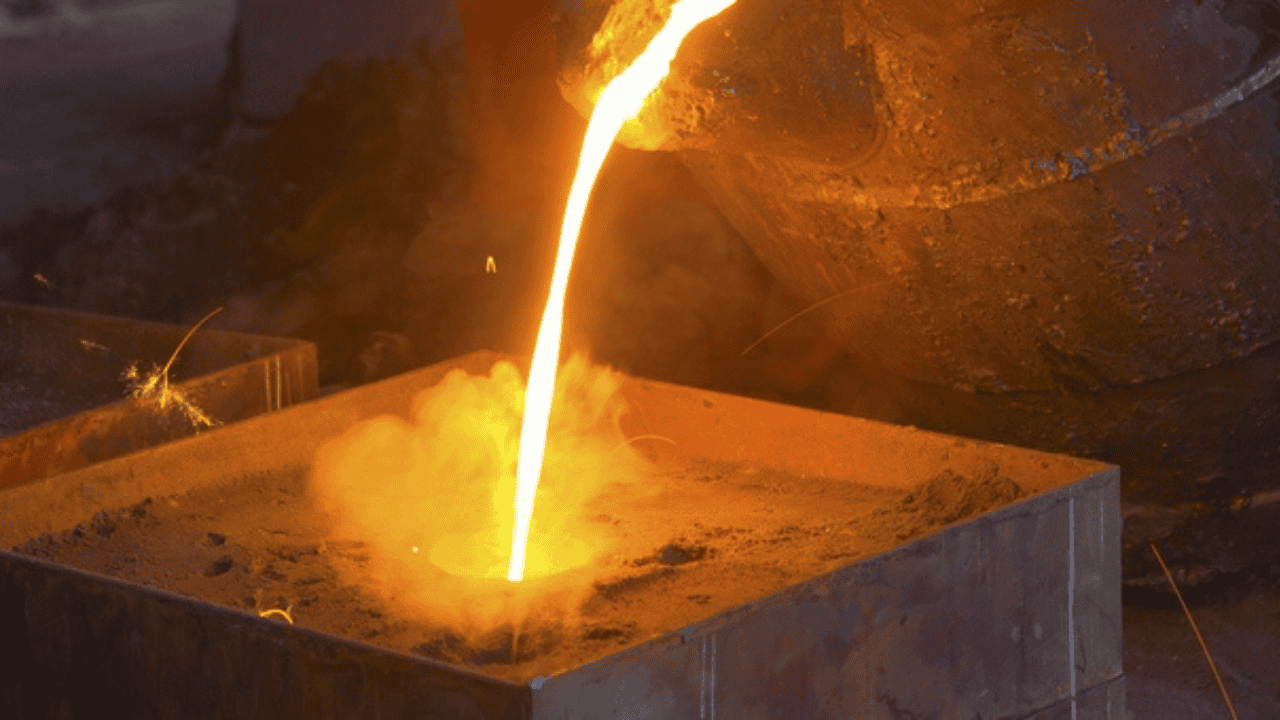

Injection
When your Zamak material has been completely melted, the next thing to do is pass it into the die casting mold under high pressure. This ensures that there are no defects such as shrinkage and gas porosity. A cold chamber or hot chamber die casting machine can be used in this effect. Hot chamber machines are mostly preferred for die casting due to Zamak low melting point and faster processing time of the machine.
Cooling and Solidification
After injection into the die casting mold, the molten Zamak material is allowed to cool off and solidify within the Zamak die casting machine using a cooling system. This cooling system within the Zamak die casting machine helps to control the solidification rate, ensuring proper microstructure formation, reducing internal stress and possible defects.
Ejection
Once the molten metal has solidified, the die halves are separated and with the aid of ejector pins the cast part is ejected out of the die cavity. Utmost care must be given during the ejection process to avoid damaging the part.
Trimming and Finishing
Although the Zamak die casting is known to produce highly detailed parts, its excellency depends majorly on the expertise of the machinist. After ejection, excess materials such as flash and runners are trimmed off. Also, secondary finishing processes such as polishing, plating, and painting are carried out on the parts to obtain a more enhanced surface finish.
Quality Control
Before packaging and distribution, each Zamak ingot cast component is checked for defects such as shrinkage and porosity. Some non-destructive testing (NDT) techniques like X-ray inspection, visual examination, and dimensional measurement ensure the final product meets industry standards.
Post-Treatment
This process is optional and not necessary. Remember that Zamak die casting can produce components with smooth surface and aesthetic appeal. But some form of post-treatment can still be applied on the casts to enhance the Zamak corrosion resistance, aesthetics, and wear properties.

Advantages of the Zamak Die Casting Process
High Precision
Zamak die casting achieves excellent precision of components due to the use of high-pressure when injecting the molten metal into a designed die casting mold. Parts with tight dimensional tolerance, often within ±0.02 mm can be designed making the process suitable for applications requiring intricate details and consistency such as interlocking components, thin-walled structures, and engravings.
Versatility
Zamak die casting is a flexible manufacturing process that is employed across multiple industries like the automotive, electronics, and consumer goods for the production of both small and large components. It also has an ease of customization. This means that Zamak die casting manufacturers can modify die casting mold designs to be able to produce parts according to specific applications.
Excellent Mechanical Properties
Having excellent mechanical properties, Zamak ingot offer high tensile strength, impact resistance, and good ductility. The alloy’s ability to withstand mechanical stress while maintaining dimensional stability ensures that parts produced through Zamak die casting are reliable and long-lasting. Unlike brittle materials that may crack under stress, Zamak alloys can absorb impacts without breaking.
Strong Dimensional Tolerance
Another advantage of Zamak die casting is its capacity to manufacture parts with precise and accurate dimensions. This is possible as a result of the minimal thermal expansion and contraction of Zamak alloy during cooling and solidification. It is therefore important to create and condition the cooling system during the manufacturing process to prevent warping and distortion.
Cost-Effective
Zamak die casting manufacturing process produces near-net-shape components that require minimal or no secondary finishing therefore reducing overall production costs and material consumption. Also, due to the high precision rate of the process, there is very little material waste during production making it cost-efficient.
Excellent Surface Finish
Cast components obtained by Zamak die casting usually have smooth and uniform surfaces that would need little post-processing. This is due to the fact that the fine grain structural properties of Zamak 3 used in the process contributes in achieving superior finishes, making them ideal for decorative and aesthetic applications.
Disadvantages of the Zamak Die Casting Process
Lower Strength Compared to Other Alloys
The Zamak alloys are stronger when compared with pure aluminum. But they do not match the tensile and yield strength of other materials like steel, brass, or some other aluminum, especially the high-grade aluminum alloys. This obvious limitation makes it not suitable for applications that require strength and ability to withstand extreme forces and heavy loads. For example, the structural parts of a bridge or aircraft require a material with higher strength than Zamak.
High Initial Tooling Cost
Highly specialized steel molds are needed for Zamak die casting. This ensures that complex and intricate part designs can be achieved consistently. Now, due to the many machining processes which include CNC milling and electrical discharge machining (EDM) involved in the production of these precise molds, the initial cost for setup is relatively high. It can therefore be less economical for small-scale production.
Limited Alloy Variation
Due to the relatively fixed compositions of the components (aluminum, zinc, magnesium, and copper) of Zamak alloys according to industry standards, it doesn’t offer much room for flexibility of its composition as opposed to other alloys.
For example, a Zamak die casting manufacturer having understood the chemical properties of Zamak alloy is most likely to go for an aluminum or steel alloy that can be easily adjusted when looking for materials with high-temperature performance. But Zamak alloy has a fixed property and trying to modify it might result in issues like increased porosity or ruin its flow characteristics.
Prone to Creep Under Constant Load
Creep is a significant disadvantage in the Zamak die casting process because it leads to the gradual and permanent deformation of a cast part over time when subjected to continuous stress. This deformation can also result in loss of dimensional accuracy, misalignment of mating components, and compromised functionality of the part. In large-volume production, minimal changes can accumulate and impact overall product reliability and optimal performance.
Reduced Strength at High Temperature
Reduced strength of Zamak alloy during die casting could be as a result of high temperature. It causes a degradation in the structural integrity of alloy, leading to deformation, softening, or creeping under load. This makes the process not suitable for applications that require prolonged heat exposure.

Applications of Zamak Die Casting
Consumer Electronics
Consumer electronics manufacturers leverage Zamak die casting in the production of a variety of high-precision, complex parts. Some of these components include internal frames for smartphones, laptops, housing connectors used in cables, tactile interfaces such as power buttons, volume controls, internal brackets, and structural supports.
Furniture Parts
Introducing the Zamak die casting into furniture making has a way of combining functionality with an attractive finish. It is an ideal process used in the manufacture of door handles, drawer pulls, cabinet knobs, and also mounting brackets used in assembling furniture. Zamak die casting provides tight tolerance, smooth finish, intricate designs, and high dimensional accuracy to all furniture parts.
Plumbing Appliances
Zamak die casting process has the ability to produce detailed surfaces that are corrosion-resistant, a major feature required for plumbing parts. Several plumbing fixtures that are made by die casting include components like faucet bodies and handles, showerheads, and various pipe fittings (such as valves, couplings, and connectors).
Conclusion
Zamak die casting is a widely known effective and efficient manufacturing process that offers precision, excellent dimensional stability, and enhances the mechanical properties of cast parts. If you would like to integrate the Zamak die casting into your manufacturing processes, it is advisable that you reach out to qualified and experienced manufacturers like Hmaking to get a quote.


