
As an auto parts manufacturer, one of the main components you can efficiently produce through die casting is the die cast engine block.
In this article, we explain how a die-cast engine block is produced, the materials used, production stages, and application areas.
How Is a Die Cast Engine Block Formed?
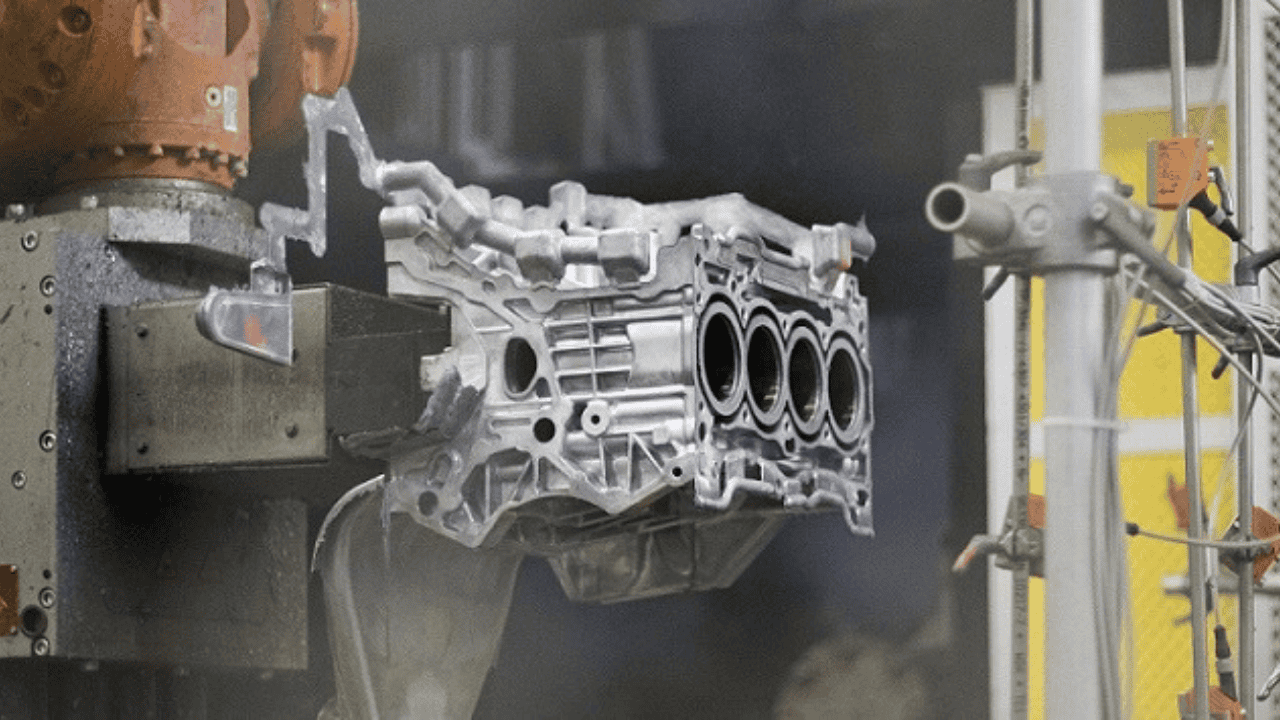
The manufacturing of a die-cast engine block begins with a suitable engine mold made of a high-temperature-resistant material and molten alloy, which can be aluminum or cast iron.
The process involves the injection of molten alloy into a suitable mold.
Because of the high injection pressure, the molten material fills all the mold cavities resulting in the formation of a die-cast engine block in seconds!
The most suitable method of producing die-cast engine blocks is by cold chamber die-casting. This is because it allows for effective control of temperatures for efficient melting of metal alloys and the casting process.
Die Cast Engine Block Materials
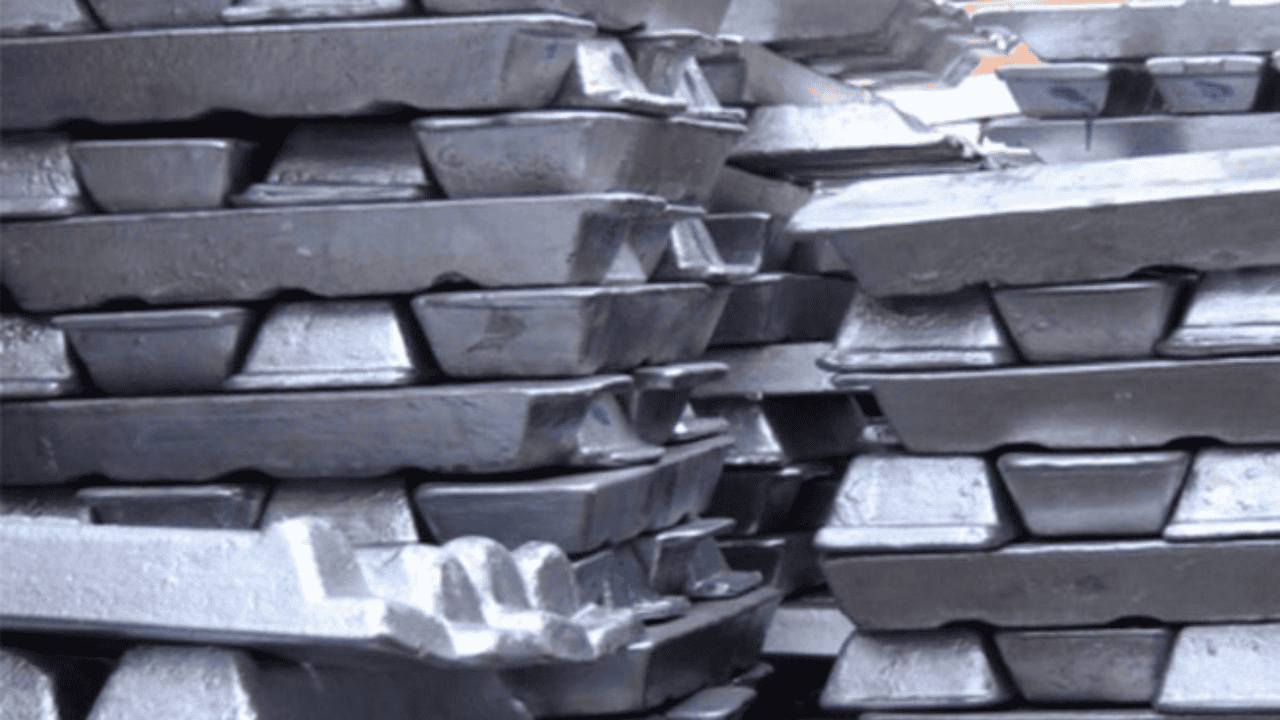

The two common materials you will require for your die-cast engine block manufacturing are aluminum and cast iron alloys.
Before we discuss the steps involved in engine block die-casting, let’s find out the benefits and limitations of choosing Aluminum alloy or cast iron as your engine block material.
Why Aluminum for a Die Cast Engine Block?
Aluminum die-cast engine blocks have the following benefits that are linked to either the production material(aluminum alloys) or the die-casting process.
Al Die Cast Engine Blocks are Strong But Lightweight
Aluminum alloys used in engine block die-casting are light in weight but strong. The low density is due to aluminum while the other alloy elements such as copper, zinc, and magnesium enhance the material’s strength and other properties.
This makes it possible to produce cast engine blocks with thin walls yet strong enough to support its engine’s operations.
Excellent Resistance to Corrosion
Aluminum alloys for a stable and protective layer of aluminum oxide. So, aluminum alloy die-cast engine blocks are desirably resistant to corrosion.
Therefore, the engine blocks can be safely used in vehicles operating on harsh roads or weather conditions.
Die Cast Aluminum Engine Blocks are Environmental-friendly
Engine block die-casting does not result in the production of waste materials. This is because the molten alloy material is effectively utilized.
Further, old or damaged engine blocks are recyclable. This makes the production of die-cast engine blocks environmentally friendly and popular!
Design Freedom and Performance Efficiency
With the die casting of engine blocks, different car or engine manufacturers have the flexibility to come up with their unique designs. This makes the production of high-performance engine blocks possible because manufacturers can come up with innovative designs and improvements.
Engine Block Die Casting is Highly Efficient & Cost-effective
You can efficiently and accurately die-cast engine blocks in large quantities. This is because the production process is not as demanding or as intricate as some machining techniques. In just a single process, you can have your engine blocks ready in no time, and at a low cost!
Therefore, as a manufacturer, if you are to reap from economies of scale, engine-block die-casting is the better way!
Limitations of Al Alloy in Die Cast Engine Blocks:
Aluminum Alloys are lightweight and less tough than iron alloys. Therefore, they are not suitable for producing engine blocks for heavy-duty vehicles.
Read more on die-cast aluminum alloys here.
Why Choose Cast Iron for a Die Cast Engine Block?
There are instances where strength and durability are more critical than the need for a lightweight aluminum alloy engine block. That’s where iron alloys or cast iron come in.
For diesel engine blocks that are meant for heavy-duty vehicles enhanced aluminum alloy or cast iron is your ideal material.
So, why cast iron for your die-cast engine block?
Here are the reasons:
- Cast Iron is readily available and therefore, less expensive compared
- It boasts high Strength and durability as it can tolerate high temperature and pressure
- You can bore large diameters on cast iron engine blocks to accommodate larger pistons for more power!
- The iron alloy has excellent thermal conductivity for better engine cooling during operation
- Cast iron has a satisfactory dumping property. This ensures cast engine block vibrations remain low.
Key Limitations:
Cast iron is heavy and therefore not suitable for die-casting engine blocks of fast-moving vehicles. Heating and machining of cast iron will cost you more compared to aluminum alloys. Again, it is only ideal for low-volume production.
The Steps In Die Cast Engine Block Production Process
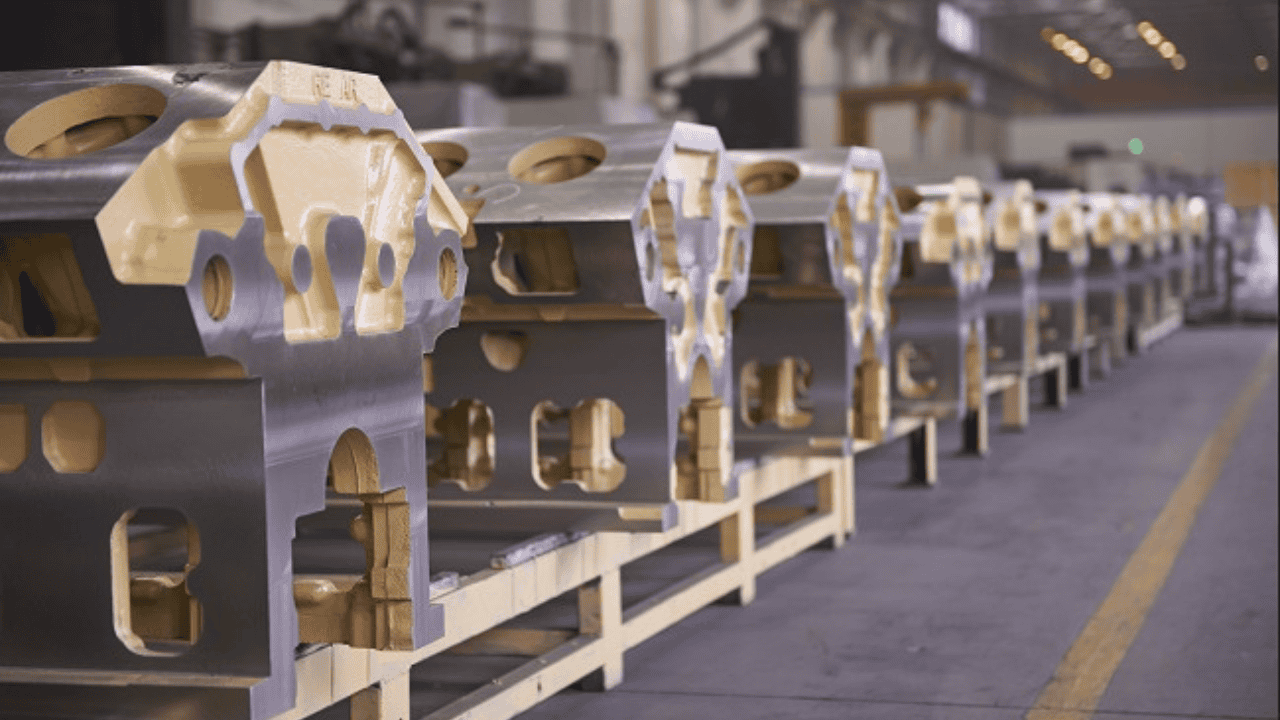

Below are the main steps you need to go through during your engine block die-casting process:
Step 1: Die Cast Engine Block Mold Design
This is the initial stage of your production which involves using CAD software to develop the digital design of the engine block. Alternatively, your customer may provide you with the design for your production. The mold design is to guide you in developing an accurate mold.
Step 2: Engine Block Mold Sand-casting
The second step is green sand-casting of the engine block based on the provided digital design. The mold is normally made from a mixture of zircon sand, with a suitable binder and hardener. This is a cost-effective mixture capable of withstanding the high temperatures during the die-casting process.
For high-volume production of die-cast engine blocks with tight tolerances and superior finish, you can consider a steel mold.
Step 3: Mold Preparation
Thoroughly clean the mold to remove any particles or debris stuck on its surfaces. Then, inspect the mold’s surface for defects such as cracks or physical deformations.
You must apply a coat to the mold’s surface to ensure that the molten material does not stick to it and to allow for easy demolding.
Step 4: Material Selection and Preparation
After accurately and successfully preparing the mold, you need the molten metal for the type of die-cast engine block you intend to produce. You may also need to add other improvement elements.
Material Selection
Your choice of engine block material depends on the specifications or standards you get from your customer. The material should be of high quality and free from contamination.
For heavy-duty engine blocks, you will need cast iron. Aluminum alloy is a suitable option for standard engine blocks.
Degassing
It is also necessary that you effectively degas the molten alloy material. This is necessary because trapped air can create defects in your engine block during the casting process.
Heating Temperature Control
You must also control your alloy heating process to ensure that your molten metal is of the desirable viscosity, and can smoothly flow into your prepared mold. Therefore, your furnace should have the necessary temperature monitoring and control equipment.
More details on the types of aluminum alloys used in die-casting are here.
Step 5: Engine Block Casting Process and Cooling
This stage involves careful pouring of molten alloy into your mold where it goes through the cooling and setting process. The cooling process must be uniform as sudden or inadequate cooling can cause defects or deformations on your formed engine block.
Step 6: Demolding, Trimming, and Machining
With your engine block fully cooled inside the mold, the next step is the demolding process. This is the removal of your die-cast engine block from the mold.
What follows is the trimming of extra material along the mold seams.
Step 7: Post Production Machining
This step entails machining your die-cast engine block to achieve precise dimensions. This stage involves CNC machining processes such as cylinder boring and honing.
Step 8: Quality Inspection
This is the final stage of your die-cast engine block production. It involves inspection of the engine block’s dimensions to verify if it conforms to the design parameters.
High-precision analysis tools and equipment are used to ascertain that your die-cast engine block is free from surface or internal defects.
After all the quality inspection parameters are fulfilled, the block is certified as suitable for use and, and packaged for delivery to the customer.
Applications of Die Cast Engine Blocks

Die-cast engine blocks are used as the main engine component in:
- Sports/Racing Cars
- Motorbikes
- Private cars
- Passenger vehicles
- Heavy-duty trucks
- Planes
Conclusion
Die-cast engine block manufacturing requires a careful selection of materials and preparing a flawless mold. Each stage of the production process requires expertise.
HM has over 20 years of experience in die-casting, CNC Auto parts manufacturing, and post-production processes.
Contact us for high-quality die-cast engine blocks customized to suit your application needs.
Links You May Like
- Aluminum Cylinder Head Series
- Casting Vs Forging: Definition, Types, Processes, and Applications
- Hot Chamber Die Casting: How It Works, Applications, and Limitations
- Ultimate Guide to Vaccum Die-casting
- Structural Die Casting: Meaning, Benefits, and Applications
- Top 10 CNC Machining Centers Factory in China
- Metal Materials for Die-casting


