Tolerance stacking performs an important part in design and engineering. Its proper management guarantees that production processes are reliable and accurate. In this blog post, we are going to cover types of tolerance stacking, methods of tolerance stack up analysis and best practices for managing tolerance stacking.
What is Tolerance Stacking?
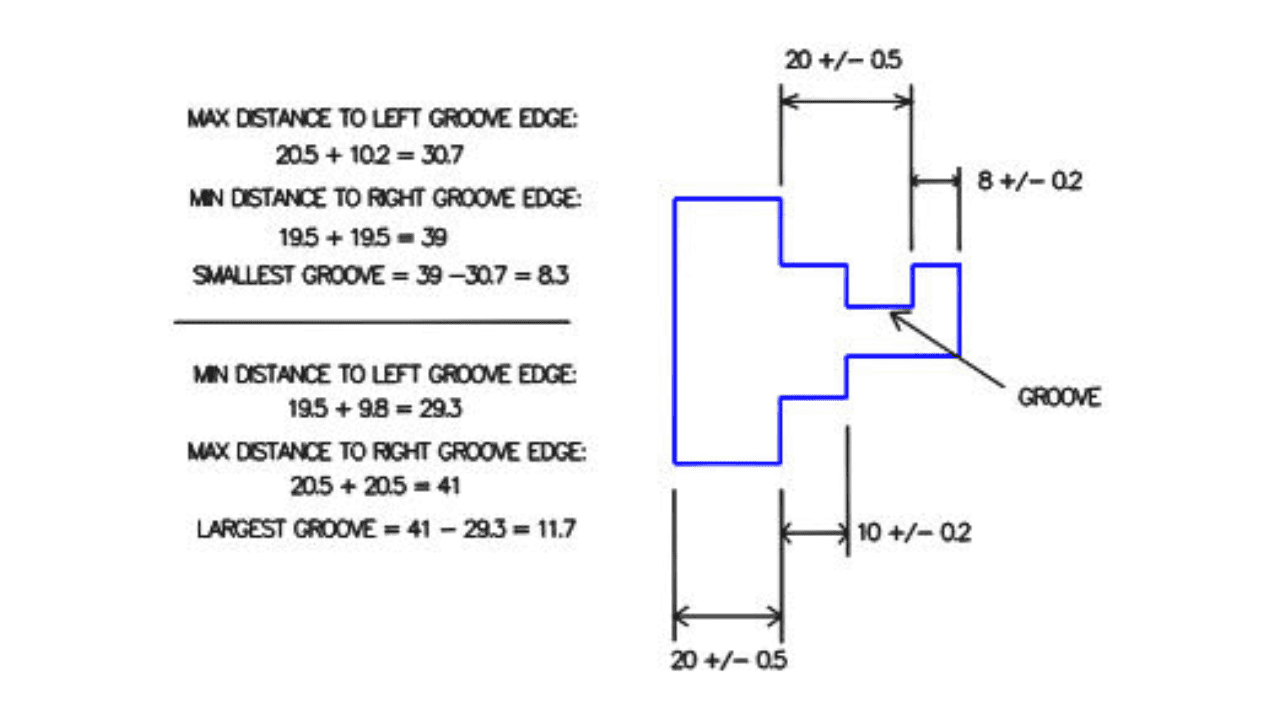
Tolerance stacking accounts for the accumulation of variation when multiple parts are assembled into an assembly. This engineering approach studies how small variations in each part affect the whole assembly to guarantee proper assembly and performance. It points out possible assembly issues before you start the production process.
Types of Tolerances
There are mainly 2 types of tolerances, as follows:
Dimensional Tolerances
This tolerance specify the acceptable variation range for linear measurements such as width, length, and diameter of parts. These tolerances use unilateral (+/-) or bilateral (±) format to define lower and upper limits for important dimensions. Engineers usually specify tight tolerances of ±0.05 mm or less to assure proper function and fit in precision components.
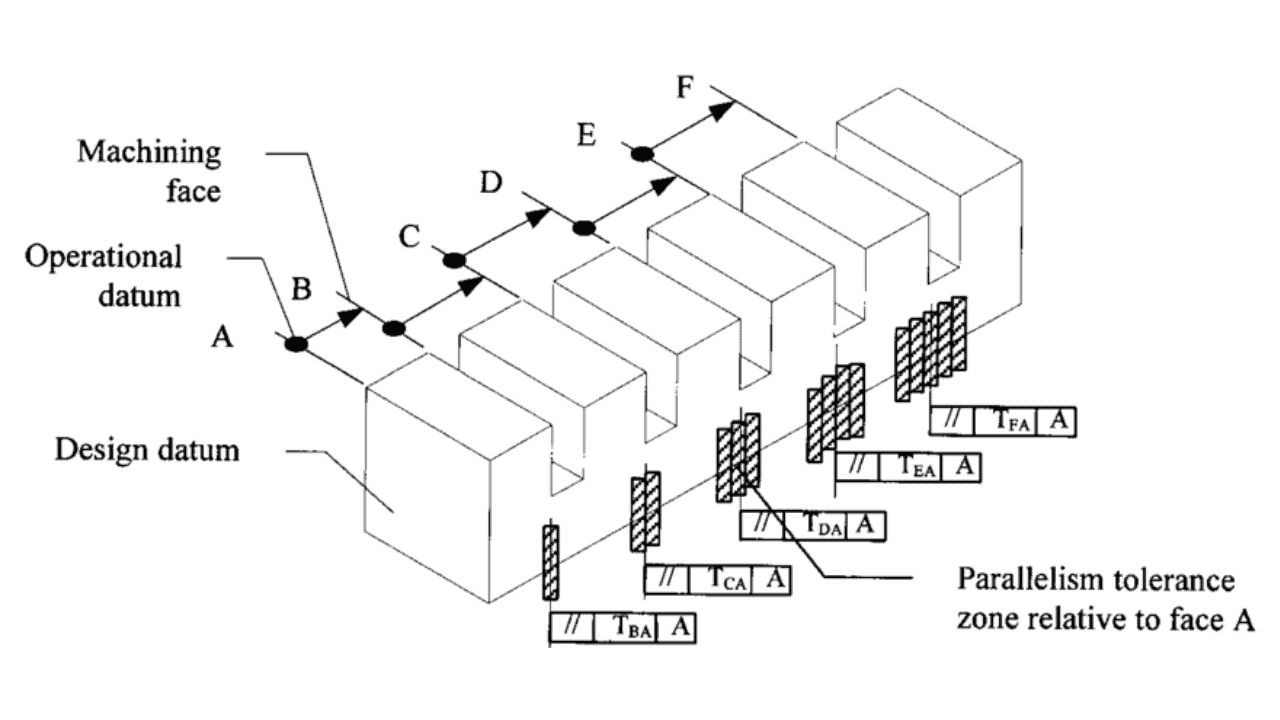
Geometric Tolerances
Geometric tolerances control orientation, location, run out and form characteristics. They use feature control frames and standard symbols to define acceptable variations in shape characteristics such as straightness, cylindricity, perpendicularity and flatness. This system guarantees proper fit and function for assemblies and uses particular tolerance zones to determine acceptable geometric deviations.
Sources of Tolerances
Manufacturing Processes
In manufacturing processes, dimensional variations occur naturally due to the capabilities and limitations of the process. For example in CNC machining you may face accuracy limitations because of machine vibrations, tool wear and thermal effects. Similarly dimensional inaccuracies can occur in casting process due to uneven cooling and mold shrinkage.
Material Properties
The ability of a part to maintain its dimensions also depends on the inherent properties of materials you use such as hardness, elasticity, thermal expansion, and shrinkage rates. Thermal expansion and contraction cause dimensional variation when materials expand with heat and contract as they cool. Besides that highly elastic materials can temporarily deform under stress which in turn causes dimensional variations in the shape of part.
Methods of Tolerance Stack-Up Analysis
Different tolerance stack up analysis methods are used to assure correct assembly and performance. Some designs require a careful approach while others may benefit from probabilistic calculations. The two main methods are.
Worst-Case Analysis
This method calculates the maximum and minimum tolerance stack up assuming that all features are at their extreme limits. It guarantees 100% assembly success as well as zero rejection rate but it needs extremely strict individual tolerances which increases the cost of manufacturing. Thus it is appropriate for applications where failure is unacceptable such as in aerospace or medical devices.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis combines tolerance distributions instead of extreme limits to predict assembly variation. You can use methods such as Root Sum of Squares (RSS) to calculate the standard deviation of stack-up whose formula is T_tot = √(T₁² + T₂² + … + Tₙ²). Apart from that, this approach assumes normal distribution of tolerances and permits you to use wider component tolerances.
Best Practices for Managing Tolerance Stacking
Clear Engineering Drawings
Your engineering drawings should focus on important features that need particular tolerances and avoid over dimensioning. You should use GD&T symbols carefully to guarantee clarity in your drawings. Moreover a clean drawing automatically controls auxiliary feature dimensions and also keeps focus on tolerance chains that can impact the assembly functionality.
Practical Tolerance Specifications
You should set tolerances based on ISO 2768 and ISO 286 for general dimensions and important fits respectively. You should apply tight tolerances only for precision features such as bearing surfaces and use medium tolerances for non critical features. This balanced approach will help you improve manufacturing costs.
Be Mindful of Manufacturing Capabilities
You should match your tolerance specifications with the capabilities of your available manufacturing machine. A modern CNC machine can reach positional accuracy of ±0.002mm to ±0.005mm. You can reach even tighter tolerances with particular tooling. Additionally you should take environmental control into account as ±1°C of temperature variations can affect the dimensional stability of your components.
Modern Tools and Software
You can perform automated tolerance stack up calculations and simulations by using advanced CAD tools like SolidWorks TolAnalyst and CETOL 6σ. These programs permit you to analyze 3D assemblies with integrated GD&T capabilities. So you can validate tolerance specifications in real-time.
Adherence to GD&T Standards
You should follow ISO 1101 or ASME Y14.5-2018 standards if you want consistent geometric tolerancing. These standards give you unified symbolic language in order to communicate design intent. Make sure you use the appropriate feature control frames and define the datum reference system correctly. This standardization decreases the chance for interpretation errors across manufacturing and design teams.
Continuous Collaboration
Design, quality and manufacturing teams should cooperate with each other during product development cycle. You can improve your tolerance specifications by regular design reviews with your manufacturing engineers. Moreover you should do process capability studies and analyze CMM data with your cross functional teams. This way you can improve tolerance assignments based on actual production metrics.
Conclusion
A systematic approach is necessary for effective tolerance stacking management where both geometrical and dimensional controls work with appropriate analysis methods. Standardized practices, cross functional collaboration and modern tools have made optimal tolerance specifications possible.
If you want your parts to be manufactured with precise tolerances and expert stack up analysis, then hMaking is best option. You can contact us anytime.
Common Questions
- Why is tolerance stacking important in manufacturing?
Tolerance stacking allows components to fit and function in assemblies correctly. It predicts cumulative dimensional variations before production begins to prevent costly manufacturing errors. - How does worst-case tolerance analysis differ from statistical tolerance analysis?
Worst case analysis works on assumption that all tolerances are at extreme limits at the same time whereas statistical analysis calculates probable variations based on normal distribution by using Root Sum Squares (RSS) method. - What are the common challenges faced when performing tolerance stack-up analysis?
These challenges include material properties, absence of accurate data, overlooking temperature effects and wear factors. - How can over-dimensioning in engineering drawings affect tolerance stacking?
Over-dimensioning increases costs and complicates manufacturing by creating redundant tolerances. It makes parts harder to produce because of unwanted tight tolerances and conflicting requirements.


