No – Titanium is not magnetic.
Although titanium is a metal with a silver color, it does not show reasonable magnetic properties. It is among the non-magnetic metals commonly available. Other non-magnetic metals are copper, silver, tungsten, and aluminum.
Of course, the non-magnetic properties of titanium can be a little intriguing. That’s why we will explain some basic facts about titanium magnetism here.
Why Titanium is Non-magnetic Metal

The magnetic properties of a metal depend on the crystalline structure and availability of electrons.
In titanium, there are no unpaired electrons. Besides, titanium in its pure form has a crystalline structure. As a result, it does not show any magnetic properties like ferromagnetic materials.
Therefore, when you place titanium in a magnetic field, there will be hardly any form of interaction. For this reason, we classify titanium as a diamagnetic material.
Facts Diamagnetic Material
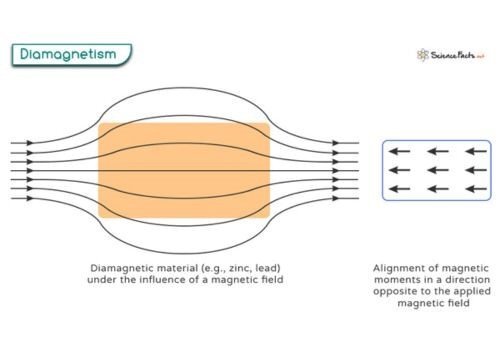
Diamagnetic materials do not have magnetic dipoles. However, whenever there is a magnetic field they experience a repulsive force.
Alternatively, you can say these materials experience magnetization in the direction opposite to that of the magnetic field. Ideally, that is the unique phenomenon you expect from titanium metal.
Magnetic Properties of Alloyed Titanium
Although pure titanium is a diamagnetic material, you can add certain ferromagnetic elements. As a result, you may end up with a paramagnetic material.
In such situations, your alloyed titanium will tend to have weak magnetic properties. That is, when you subjected alloyed titanium to a magnetic field, it will experience weak magnetization.
The magnetization is usually in the direction of the magnetizing field. Don’t get this wrong, the paramagnetic behavior is for alloyed titanium.
Under certain circumstances, alloyed titanium magnetic properties may be similar to ferromagnetic materials. It will depend on the chemical composition of the alloying element.
Factors Affecting Non-magnetic Properties of Titanium

There are rare occasions that you may experience unique magnetic behavior in titanium. Usually, this can be attributed to several factors such:
Titanium with Impurities
Titanium’s magnetic properties may be affected by certain impurities such as iron. Remember, iron is a ferromagnetic material. Therefore, it gets magnetized and can be attracted by magnets.
When titanium contains a significant amount of iron it may behave like a ferromagnetic material.
Magnetizing Titanium
Even if you try to magnetize titanium, it will not become a magnet due to its electron configuration. Even with the strongest external magnetic field, you will end up with weaker magnetic moments. These magnetic moments cannot remain magnetized.
That is, they will not improve the net magnetic moment in titanium. Therefore, titanium will remain a non-magnetic metal.
Applications Titanium as a Non-Magnetic Material
Apart from the non-magnetic property, titanium is known for:
- Superior corrosion resistance
- Lightweight
- Superior strength
At the same time, the non-magnetic property makes titanium a perfect material for some specific applications such as:
- Medical devices manufacturing
- Making parts in the aerospace industry
- Fabricating parts in the chemical industry
- Making implants
- Equipment in desalination plants
- Any other application that does not require magnetic interference
In short, titanium is a non-magnetic material. However, impurities such as iron can make titanium possess some magnetic properties. However, this behavior is limited.
More Resources:
Titanium Melting Point – Source: HM
Titanium – Source: WIKIPEDIA


