One of the biggest demands of manufacturers across industries is how to fabricate large volumes of parts within the shortest possible time. This is why the hot chamber die casting process is a big deal. It combines speed, efficiency, and optimum quality assurance in die casting operations. In this article, we’ll explore the essentials of this technique, including its operating principles and advantages. Read on!
What Is Hot Chamber Die Casting?

Hot chamber die-casting is a metal casting process that is used to produce small to medium-sized components with high precision and excellent surface finish.
This process is highly automated requiring no human interference after the materials have been out in place. Everything about it happens in a hot chamber die-casting machine. It is an all encompassing machine that handles every part of the operation without need to move the alloy into an external equipment.
The machine can’t sustain some levels of heat. Hence, the process is fit for only elements with a low melting temperature. Examples include lead, zinc, magnesium alloy, and tin. High temperature can cause damage to the gooseneck and nozzle of the hot chamber machine.
Hot Chamber Die Casting Process
Melting the Metal Material
The first thing to do is choose the material you would need to achieve your final product, it could be zinc, lead, or magnesium. Once you’re done, place it into the furnace of the die-casting machine and allow it to melt at its required melting temperature.
One thing that makes this technique fast and efficient is that it has a built-in furnace that keeps the metal in its molten state throughout the operation. Hence no need to heat in an external chamber and transfer back to the main unit.
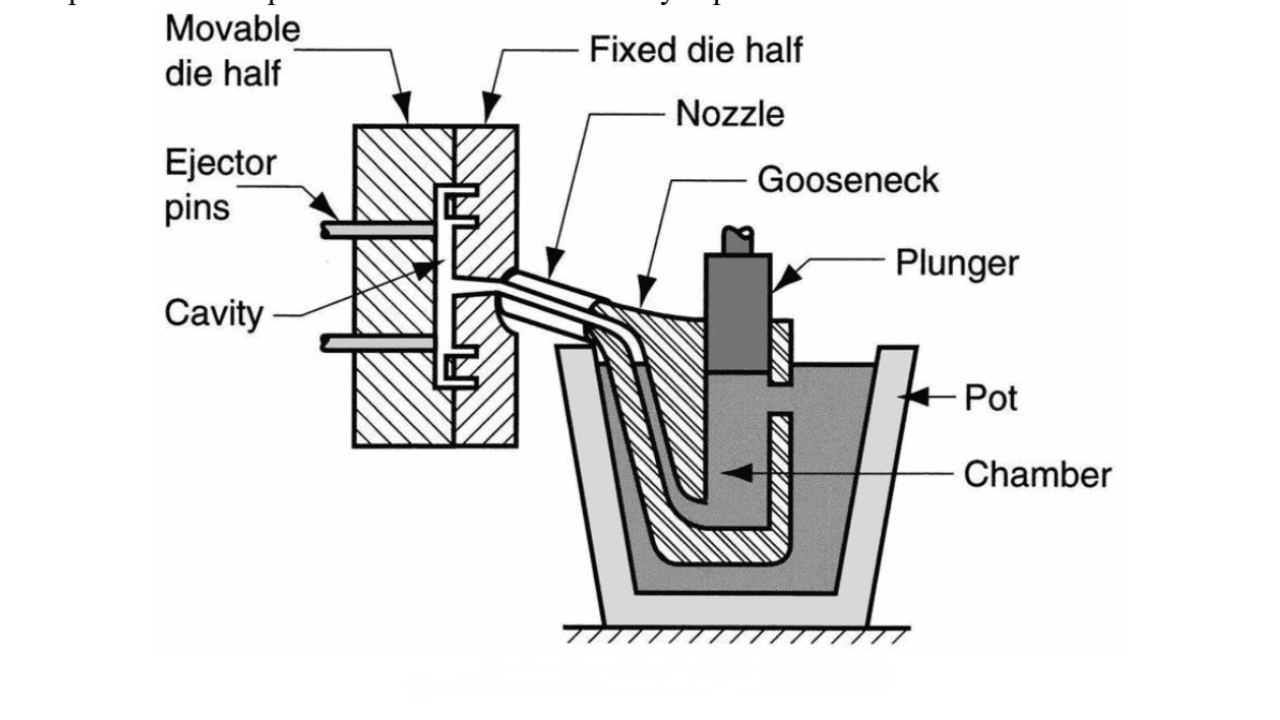
Hot Chamber Filling
Once melted, the metal is drawn from the reservoir using a gooseneck. The gooseneck is usually made with forged steel or quality cast which helps it withstand extreme temperatures and ensures a steady and consistent flow during injection. It serves as a connector between the metal bath and the mold.
Injection
This is the process of passing the liquefied material into the die-cast using a plunger. This injection process is quite similar to how a hospital syringe functions. Imagine a syringe filled with liquid drawn up through the needle and then the plunger is pushed forcing the liquid to gush out with pressure.
Likewise in this technique, the molten metal is the liquid. The gooseneck is the needle, and the hydraulic plunger can be likened to the syringe plunger which ensures all parts of the cast are filled.
Cooling and Solidifying
In this stage, the molten metal is allowed to cool to lower temperatures. There are cooling systems built within a hot chamber machine that help regulate the temperature and prevent defects. Also, the cooling time depends on the metal material used and the thickness of the cast to be formed.
Ejection
This is the final stage in a hot chamber die-casting process. Here, the solidified cast is ejected out of the die mold by a push from the ejector pins. The die mold then resets itself for continuous production. Your final cast product is ready and can undergo other post-processing finishing like polishing, coating, etc.
Metals Used for Hot Chamber Die Casting
One basic characteristic a material must have that makes it suitable for this process is its inherent ability to melt easily. Below are the materials you can use for your production.

Magnesium
Magnesium alloys are incredibly lightweight. They also have a significant high strength-to-weight ratio which makes them one of the ideal metals for this process. Among its numerous applications, it is used in the telecommunication industry to serve as a shield against radio frequency and to produce lightweight but durable components.
Zinc
Zinc’s impressive fluidity and corrosion resistance makes it highly sought after for hot chamber die casting. It also has a low boiling point and can be easily plated. Hence it’s used for manufacturing parts that require fine details and high dimensional accuracy.
Lead
As a machinist, lead alloy is your go-to when looking for materials with high density, malleability, and good corrosion resistance properties to achieve components such as plumbing, radiation-shield, and insoluble anodes.
Why Is Aluminum Not Suitable for Hot Chamber Die Casting?
The simple reason is that aluminum has a high melting point. The amount of heat required to melt aluminum is far too high and extreme for the components of a hot chamber machine. It could cause damage to parts such as the gooseneck and nozzle.
Another reason can’t be used for this technique is due to its tendency to react with iron at very high temperatures. This could result in contamination and erosion of equipment during processing, reducing its lifespan.
Advantages of Hot Chamber Die Casting
Cost-Effective
The hot chamber machine is an all encompassing masterpiece, having all its parts integrated together. Hence, you don’t need to make separate investments on these integral sections of the parts. More so, the process reduces labor cost and improves the lifespan of the components.
This can be attributed to the fact that the lower temperatures at which the hot chamber machine functions reduce thermal stress on its components, leading to less frequent servicing.
Quick Production Cycle
Having all units of the system in one piece does not only allow for easy transfer of molten metals but reduces the time it takes to do so. This, in turn, leads to a quick and easy production cycle.
For instance, after completing a particular batch of castings, instead of going through the initial process of melting your metal material in the furnace, all you need to do is transfer some molten metal from the reservoir into your die cast and start the solidification process. This type of die casting is a great way to produce large batches of components with simple or intricate designs.
Less Material Waste
Another important advantage of this process is that it produces minimal waste material because excess materials such as sprues and flash can be recycled.
That means the leftovers remaining in the sprue can undergo the entire die casting processes again. Therefore, hot chamber die coating can be considered an environmentally friendly manufacturing process.
Different Parts of Hot Chamber Die Casting Machine
Furnace
As can be easily determined, this is where the entire heating operation takes place in the hot chamber die-casting process. The whole process practically commences here and builds up to other units of the system.
Nozzle
The nozzle, usually found attached to the tip of the gooseneck, acts as a pathway between the transfer of the molten metal from the gooseneck into the die cavity. It is typically made from zinc, ceramic, zirconia, or H-13 steel because of its high resistance to corrosion and ability to withstand high temperatures.
Die or Mold
Die, or die cavity, or mold as it can be called refers to the prototype of your final design component. It is responsible for holding the smelted metal after it has been moved from the gooseneck. Hence it gives the smelted metal a defined shape, until it solidifies and is ejected.
Molten Metal Reservoir
This unit contains all of the smelted metal that will be used for the entire operation. It is directly connected to the casting machine. That way, there’s a consistent and precise repetition of the entire process.
Gooseneck
The gooseneck serves three purposes. First, as a connector between the melting pot and the die mold. Secondly, it regulates the flow of the melted metal. Thirdly, it ensures that every part of the mold is filled properly in order to prevent shrinkage defects in casting. Due to its significant role, the gooseneck has to be a material that is highly resistant to corrosion.
Hydraulic Plunger/Piston
Smelted metal has to move from the gooseneck to the die mold. This is where a hydraulic plunger comes in. It has a high suction power capable of pulling the red-hot substance into the next unit. This part is powered by a gas hydraulic cylinder.
Cooling System
This is where liquefied metal hardens up. The components of a cooling system are usually made from metal materials such as copper alloys or stainless steel due to its excellent resistance to corrosion and high thermal conductivity.
Ejector Pins
Ejector pins are very important components of the hot chamber machine. They allow for the safe ejection of casts without any defects. These pins are built into the mold and push against solid cast with controlled pressure, carefully dislodging it without breaking or causing damage.
Disadvantages of Hot Chamber Die Casting
Not Suitable for Low-Volume Production
Hot chamber die casting setup requires several units that must be prepped for each operation. This is quite expensive on a one-off basis. And even too expensive for a low volume production. However, if you’re considering a large batch operation, it’s the best choice.
Limited Material Choice
One of the downsides of the hot chamber die-casting machine is seen in how much heat it can take. While this is a defining factor of the process, it also means it can’t be used for metals that do not fall within its acceptable temperature range. If you must use materials outside of that range, you’d do so through other techniques.
Size Limitation
The structural disposition of the machine has its fair share of limitations. It cannot handle large-sized molds or manufacture heavier components. The machines are more suitable for making small – medium sized parts with high accuracy and precision.
Corrosive Effects on Parts
Some alloys used in this process can react with the machines or equipment over time. This will lead to wear and tear, and high maintenance cost. So, as a machinist, or an engineer it is very important to determine which of the molding processes between die casting and injection molding is more convenient to carry out a project. This helps you take the best approach for manufacturing and also maximize profit.
Applications of Hot Chamber Die Casting in Industries
Automotive
From engine blocks to enclosures, there are a lot of automotive parts you can produce with this process. One reason it’s a preferred technique is because of the lightweight properties of its finished products.
Industrial Machinery
Many industrial machines require components that are strong, can withstand high stress, wear, and environmental exposure. That’s where the hot chamber process can be used to produce these components such as valve bodies, pump casings, and cylinder housings with excellent dimensional accuracy and precise shape of parts.
Construction and Building
The process is also used in the construction and building industry for manufacturing housing components and structures that require strength, precision, and resistance to wear and corrosion. Examples of such components include door locks, hinges, brackets, and window latches.
Conclusion
Having understood the many concepts of the hot chamber die casting process, it is essential to know when to apply it in your production. It is considered an efficient and cost-effective manufacturing process that is ideal for producing small to medium-sized metal components with high precision. It has added so many values like rapid production cycles, material versatility, and high quality products to several industries.
Explore how this technology can enhance your manufacturing efficiency and product quality by consulting with industry experts at HM. Here, we have the best facilities and equipment to help you produce the best parts for your machines. Contact us now to get started.


